Classification Of Prodrug.
IDEAL REQUIREMENTS OF PRODRUG
An ideal prodrug must meet the following requirements
a) The prodrug should be inactive or less active than the parent compound.
b) It should not have intrinsic pharmacological activity.
c) The linkage between the drug and the carrier must be cleared in-vivo.
d) The carrier molecule released in-vivo must be non-toxic.
e) The metabolic fragments of carrier molecule apart from the active drug should be non-toxic.
CLASSIFICATION OF PRODRUG
Depending upon the constitution, lipophilicity, method of bioactivation and catalyst involved in bioactivation, prodrugs are classified into two categories.
a) Carrier linked Prodrugs
b) Bio-precursors
Carrier linked prodrugs (simple prodrugs) are the ones where the active drug is covalently linked to an inert carrier or transport moiety. Such prodrugs modify the lipophilicity of the compounds. Carrier linked prodrug can be subdivided further into bipartate, tripartate and mutual prodrug.
A bipartate prodrug is a prodrug comprised of one carrier attached to the drug. When a carrier group is connected to a linker arm, which is connected to the drug, the term tripartate prodrug is used. A mutual prodrug consist of two, usually synergistic, drug attached to each other.
Bio precursors are inert molecules obtained by chemical modification of the active drug but do not contain a carrier.
For example :- if the drug contains a carboxylic acid group, the bio precursor may be primary amine, which is metabolized by oxidation to the aldehyde, which is further metabolized to the carboxylic acid drug.
The prodrugs are also classified according to the functional group.
They are:
1. Carboxylic acid and Alcohols
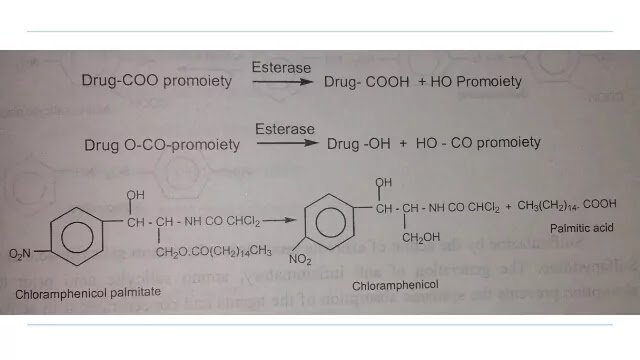
Prodrugs of carboxylic acid and alcohol functionalities can be prepared by conversion to esters. The esters can be easily hydrolyzed by esterase enzymes (lipase, cholesterol esterase, acetylcholinesterase, carboxy peptidase) present in plasma and other tissues to give active drug.
2. Amines
Derivatization of amines to give amide has not been widely used as a prodrug because of high chemical stability of amide and lack of amidase enzyme necessary for hydrolysis. A more common approach is to use Mannich bases as prodrug form of amines.
Example :
Hetacillin is a prodrug form of Ampicillin in which amide nitrogen and a amino functionalities have been allowed to react with acetone to give a Mannich base [imidazolidione ring system). This decreases the basicity and increases the lipophilicity and absorption.
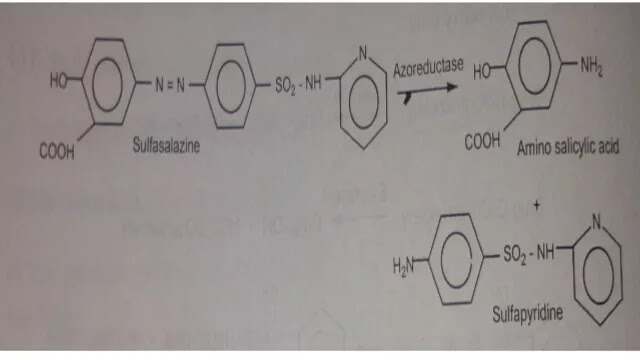
3. Azo Linkage
Amines are derivatized to azo linkage prodrug occasionally
Example :-
Sulfasalazine by the action of azoreductase release the amino salicylic acid and Sulfapyridine. The generation of anti inflammatory, amino salicylic acid prior to absorption prevents the systemic absorption of the agents and concentrates it in active site.
4. Carbonyl moiety
Carbonyl functionalities such as aldehyde and ketones conversion to prodrug have not found wide clinical utility. These are converted into derivatives in which the sp carbonyl carbon is converted to a sp hybridized carbon attached to hetero atoms. These prodrugs are reconverted to carbonyl compound by hydrolysis. For example Hexamine releases formaldehyde in the urine (acidic PH), which acts as an antibacterial agent
👉first Order Reaction, Order Of Reaction, Chemical Kinetics :- click here
👉Solid state decomposition, Order of Reaction, Chemical Kinetics :- click here
👉What is Half Life and Shelf Life, Order of Reaction, Chemical Kinetics :- click here
👉Apparent Zero Order Suspension, Chemical Kinetics, Physical Pharmaceutics :- click here
👉Zero Order Reaction, Chemical kinetics :- click here
👉ORDER OF REACTION, Chemical Kinetics Free PDF Note, Pharmacy Free PDF Book :- click here
👉ORDER OF REACTION, Chemical Kinetics Free PDF Note, Pharmacy Free PDF Book :- click here
👉MOLECULARITY OF REACTION :- click here
👉PRODRUG DESIGN :- click here
👉Application Of Prodrug :- click here
👉Classification Of Prodrug.:- click here
👉PRODRUGS, :- P.Valentina. Pharmacy PDF books for students free download :- click here
👉Chemical Kinetics, CVS Subrahmanyam full PDF file. bookhata free PDF books for students. :- click here
👉Metabolism And Extraction :- click here
👉What is Protein Binding :- click here
👉General Principle of Drug Action. Medicinal Chemistry Chapter-2 :- Click here
👉Semister–V, Medicinal Chemistry E-BOOK :- Click here
👉Pharmacognocy Semister-V, PDF Book :- Click here
👉Industrial Pharmacy-I PDF book, B-Pharm 5th Semister :- Click here
👉Interfacial Phenomena By CVS Subrahmanyam √ Physical Pharmaceutics √ 3rd Semister √ Pharmacy Free PDF Books Download :- Click here
👉Pharmaceutical Jurisprudence √ 5th Semister √ Pharmacy Free PDF Book Download :- click here
👉Pharmacology of drugs acting on cardio vascular system, 5th semister Pharmacology, Pharmacy Free PDF Book Download :- Click here
👉Autocoids and Related Drugs, Pharmacology, 5th Semister, Pharmacy Free PDF Book Download :- click here
👉Drug Stability, By CVS Subrahmanyam Physical Pharmaceutics, 4th Semister, Pharmacy Free PDF Book Download :- click here
👉Rheology, By CVS Subrahmanyam Physical Pharmaceutics, 4th Semister, Pharmacy Free PDF Book Download :- click here
👉Micromeritics, By CVS Subrahmanyam Physical Pharmaceutics, 4th Semister, Pharmacy Free PDF Books For Students Download :- click here
👉What is Absorption of Drug :- click here
👉What is Distribution Of Drug ? :- click here
👉Complexation and Protein Binding By CVS Subrahmanyam, 3rd Semister, Physical Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy Free PDF Book Download :- click here
👉Drug Metabolism, Med-Chem, 4th Semister, Bookhata Free PDF Books For Students download :- click here